
According to a recent study published in APL Photonics, a research team led by Prof. LIANG Xu from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed an ultra-compact excimer laser roughly the size of a thermos bottle.
Excimer lasers are critical sources of deep ultraviolet light and are widely used in scientific research, industrial processing and environmental monitoring. However, traditional systems rely on mechanical gas pumps for medium circulation, resulting in a large size, high noise levels, and significant vibrations. These limitations restrict their application in field environments, marine exploration and airborne platforms.
To address these issues, the researchers replaced the mechanical pumps with a multi-needle corona discharge electrohydrodynamics (EHD) pump. This eliminated the need for moving parts and reduced the system's volume to Ø130 mm × 300 mm. Using a self-developed, non-invasive point Schlieren velocimetry technique, the researchers measured a gas flow velocity of 1.27 m/s inside the laser cavity. Operating at 100 Hz, the system achieved a gas refresh rate of 6.35, delivering pulse energies in excess of 2 mJ while maintaining exceptional energy stability, with a relative standard deviation as low as 1%.
The researchers also observed a unique explosive transition behavior in the laser's pulse energy under certain conditions. Through complex photochemical reaction analysis of the XeCl excimer network, they discovered that this phenomenon is linked to a threshold-driven burst in photon flux, revealing the microscopic mechanism behind shifts in macroscopic laser performance.
Furthermore, the team developed an interpretable machine learning model capable of predicting energy transitions across a wide range of operating parameters.
This study provides valuable support for the optimization and control of ultra-compact excimer laser systems in practical applications.
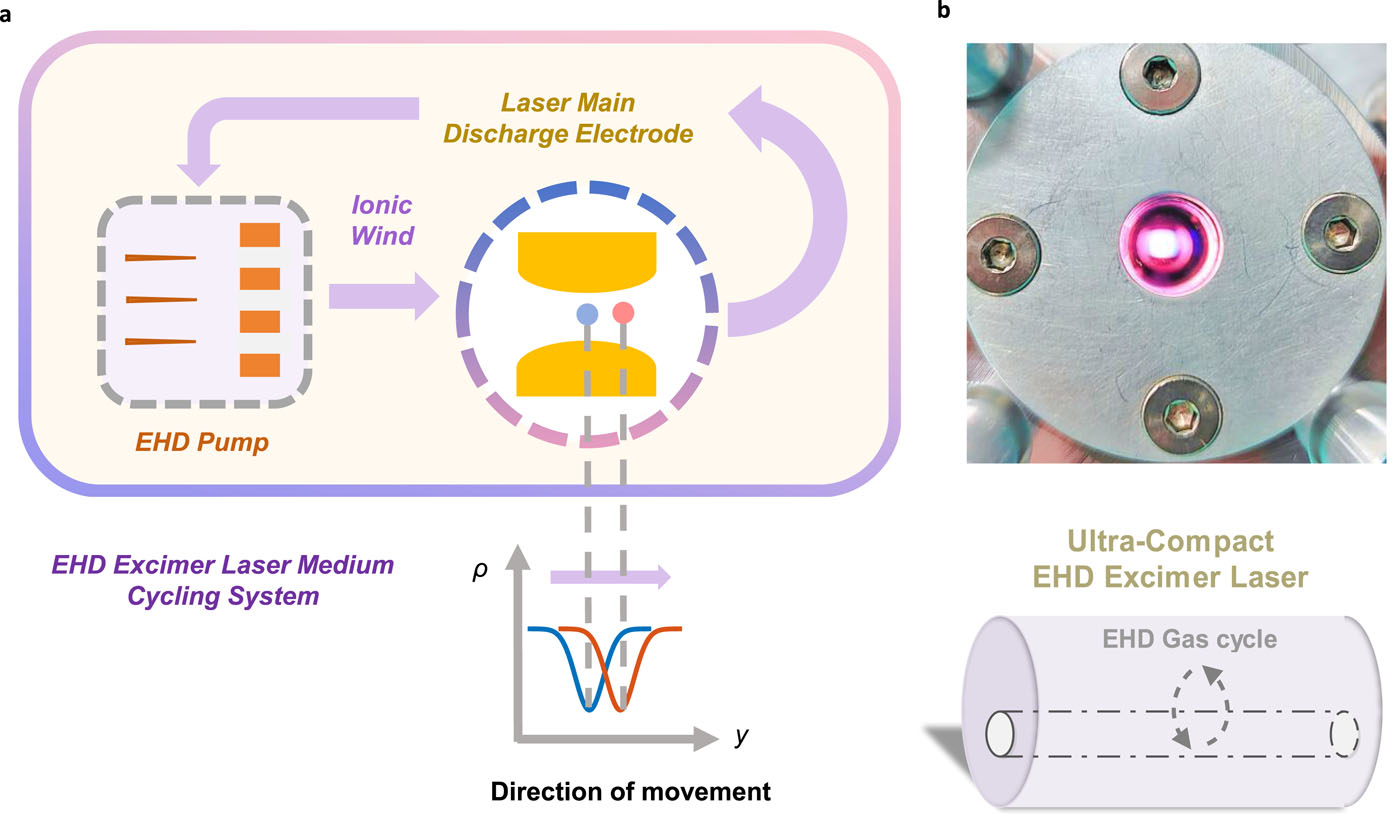
Ultra-compact excimer laser based on EHD (Image by SHAO Jingzhen)
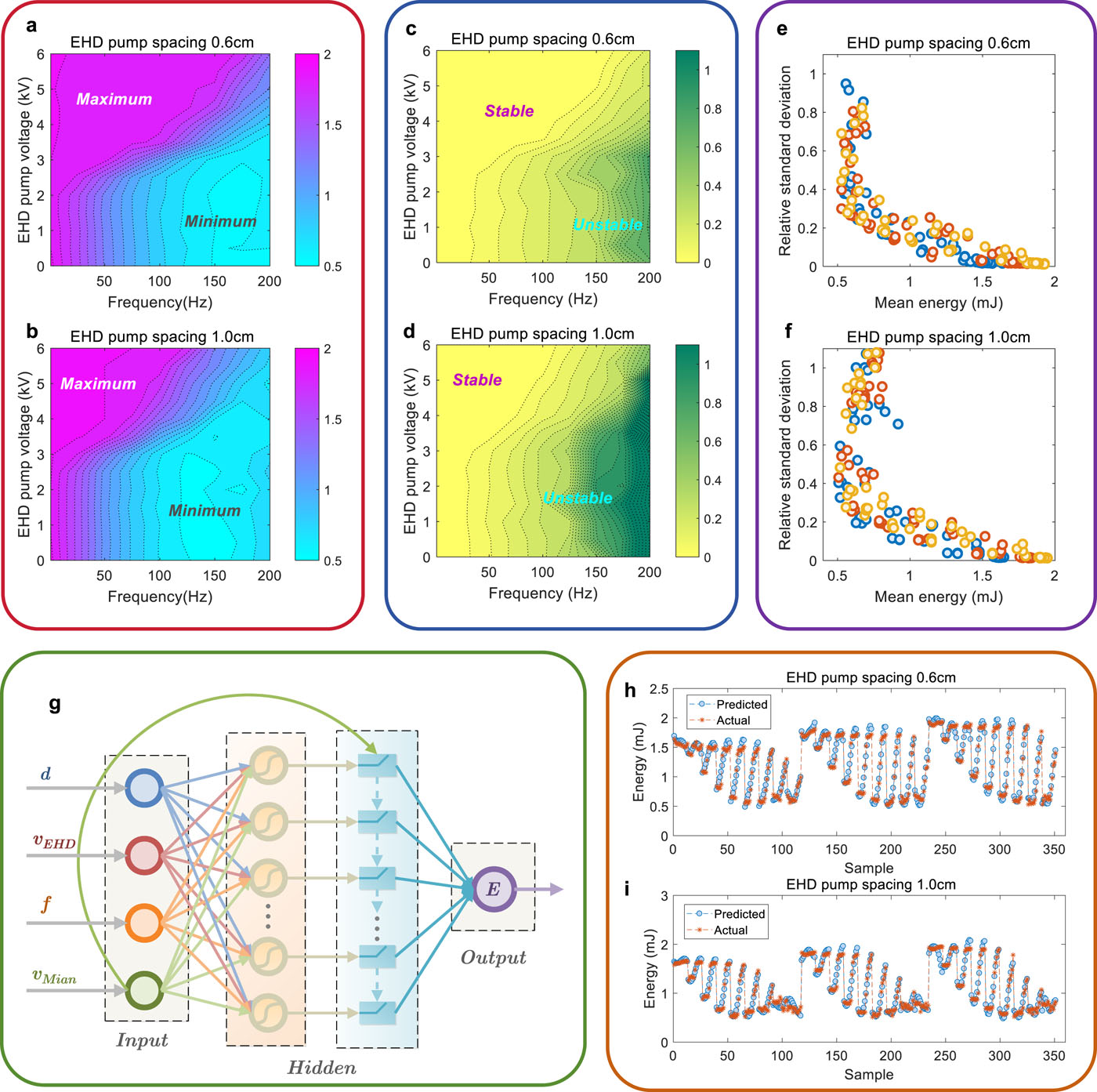
Mechanism analysis and machine learning prediction of ultra-compact XeCl laser energy explosive transition phenomenon (Image by SHAO Jingzen)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

